Simulation of Steady, Laminar Flow Over a Backward-Facing Step
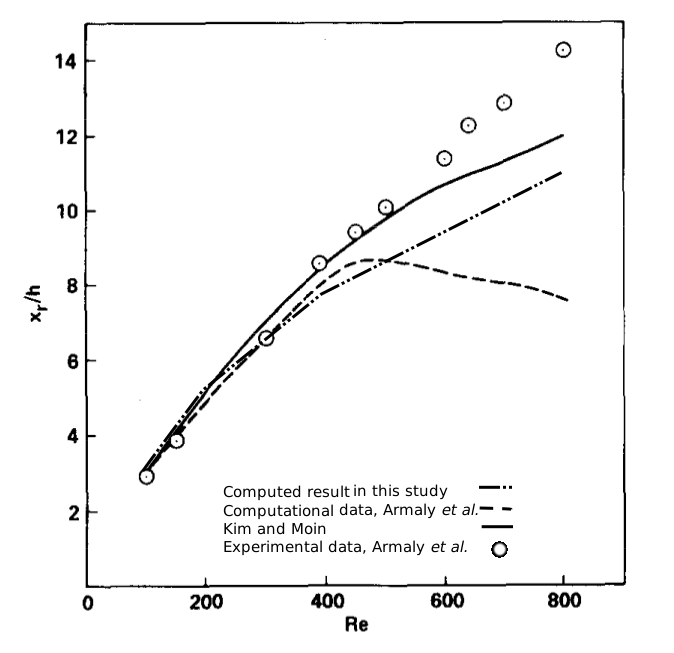
A 2D Navier-Stokes solver was developed to simulate steady, laminar flow over a backward-facing step of height $h$. The step expansion ratio=1/2 and the flow at the step was assumed to be fully developed, laminar channel flow. The Reynolds number for this flow was defined as $Re=\frac{Uh}{ν}$. The 2D incompressible Navier-Stokes equations was solved in generalized curvilinear coordinates using artificial compressibility method. A code was developed using C++ with OpenMP and also with MATLAB where three-point , second order finite differencing was used to discretize the convective and viscous fluxes in conjunction with scalar, fourth-difference, third-order artificial dissipation for stability. Dual time-stepping with a second-order backward scheme in real time and four stage Runge-Kutta time stepping was used for pseudo time. The flow was simulated for $Re_h$ = 50, 100, 200, and 400. The streamlines were plotted in the steady-state. The results were compared with the experimental data obtained by Armaly et al. [1] and the numerical solutions obtained by Kim and Moin [2]. The effects of local time stepping, implicit residual smoothing and the CFL number are investigated on the rate of convergence of the time algorithm. The effect of artificial dissipation on the accuracy and stability of the solution is also investigated. The results are in agreement with the experimental and numerical solutions of Armaly et al. and Kim and Moin.
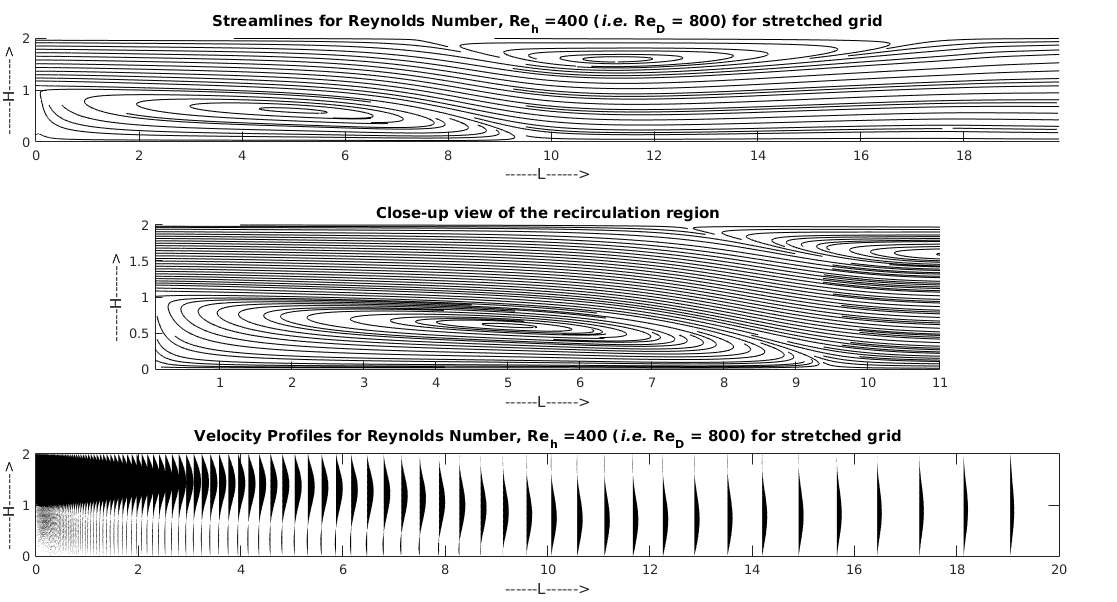
$Re_h = 400$ for Stretched Grid:
References
[1] Bassem F Armaly, F Durst, JCF Pereira, and B Schonung. Experimental and theoretical investigation of backward-facing step flow. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 127:473–496, 1983.
[2] John Kim and Parviz Moin. Application of a fractional-step method to incompressible navierstokes equations. Journal of computational physics, 59(2):308–323, 1985.
